Cloud computing is becoming an increasingly popular solution among small businesses, enabling access to advanced technologies without the need for large investments in IT infrastructure. Cloud solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and potential savings that were previously available only to large corporations. In this article, we analyze in detail what cloud computing is, what its real costs are, and whether implementing it in a small company is really worth it.

Introduction to Cloud Computing
In today's rapidly changing business environment, small businesses often have to compete with large corporations that have much greater resources at their disposal. Cloud computing technology levels the playing field to a large extent, enabling access to advanced IT solutions without having to invest in expensive infrastructure.
Just a few years ago, small businesses had to choose between outdated systems and expensive investments in computer hardware and software. Today, cloud computing offers a third way – modern, flexible solutions available in a subscription model, where you pay only for resources actually used.
According to data from reports on the state of the small and medium-sized enterprise sector in Poland, more and more companies are deciding to use cloud solutions in their daily operations. The interest in social media, cloud computing and the Internet of Things is systematically growing, especially among large and medium-sized enterprises, although small companies are also beginning to see the benefits of these technologies.

What is cloud computing?
Definition and principle of operation
Cloud computing (cloud computing) is an IT service delivery model in which computing resources are available on demand via the Internet. In this model, users do not have to invest in their own hardware or software infrastructure – instead, they rent the resources they need from external providers.
The principle of cloud computing is to transfer the entire burden of providing IT services (data, software or computing power) to the server and enable constant access through client devices. Thanks to this, data security does not depend on what happens to the company computer, and the speed of processes results from the computing power of the server.
Cloud computing works by processing computer resources in large data centers managed by cloud service providers. Customers can access these resources over the Internet using various devices – computers, tablets or smartphones.
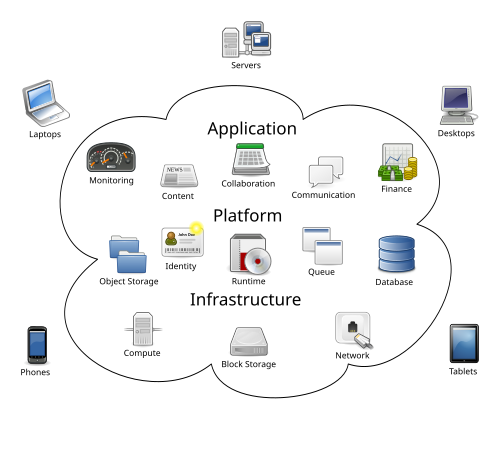
Types of cloud computing
There are several types of cloud computing available on the market, which differ in the scope of control, level of security and costs. Choosing the right model should be adapted to the specific needs of the company.
Public cloud
Public cloud is a solution in which IT infrastructure is managed by an external provider and made available to many users over the Internet. It is a cost-effective option for small businesses that do not need dedicated infrastructure. Examples include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
The main advantages of the public cloud include low implementation costs, no need to maintain your own infrastructure, and ease of scaling. However, in this model, the company has limited control over data and less ability to personalize the environment.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, providing a higher level of control and security. It is a good choice for companies in regulated sectors that require specific data security requirements.
This solution offers greater flexibility in configuring the environment according to the needs of the company, but is associated with higher costs and requires greater technical competences.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines elements of public and private clouds to create a flexible and optimized IT environment. It is ideal for small businesses that want to store some data and applications in a highly secure private cloud while also benefiting from the cost-efficiency and scalability of a public cloud.
This model allows for strategic deployment of resources – critical data can be kept in the private part, and less sensitive applications in the public cloud.

Benefits of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
Reduction of operating costs
One of the most tangible benefits of using cloud computing for small businesses is a significant reduction in costs. In the traditional model, companies have to invest in the purchase of servers, software licenses, as well as incur fixed costs of maintaining the infrastructure and hiring IT specialists. Cloud computing works in a pay-as-you-go model, which means that the company pays only for the resources actually used. The lack of need to invest in equipment also means less risk associated with its depreciation. This model eliminates the need for large initial investments, which is especially beneficial for startups and small businesses with a limited budget. Additionally, using cloud services allows you to move expenses from the CAPEX (capital expenditure) category to OPEX (operational expenditure), which is often more beneficial in terms of taxes and makes budget planning easier.Resource flexibility and scalability
Cloud computing provides small businesses with unprecedented flexibility. As business grows or seasonal changes occur, they can easily adjust the level of resources used—increasing computing power, storage space, or Internet bandwidth without having to invest in new hardware or software. The scalability of the cloud means small businesses can start with modest resources and gradually expand as their needs grow. This is a significant advantage over the traditional model, where future demand must be anticipated and often investments must be made “on the fly.” This flexibility also allows them to react quickly to market changes. If a company needs to increase data processing capacity suddenly (e.g., during the holiday season in e-commerce), they can do so almost immediately, and then reduce resources when they are no longer needed.Access from anywhere
Cloud solutions provide access to company data and applications from anywhere in the world where there is Internet access. This feature is particularly important in times of growing popularity of remote and hybrid work. Employees can access the same tools and data regardless of whether they work from the office, home or during a business trip. This facilitates team collaboration, increases productivity and allows for greater flexibility in work organization. For small business owners, it also means the ability to supervise the business from anywhere. They can monitor business indicators, contact the team or approve decisions even while away from the office, which ensures business continuity.Data security
Despite popular concerns, professional cloud services often offer higher levels of security than on-premises solutions for small businesses. Cloud providers invest significant resources in security features, such as:- • Advanced firewall and intrusion detection systems
- • Regular data backups
- • Encryption of transmitted and stored information
- • Continuous monitoring of threats
- • Compliance with international safety standards

Automatic updates
By using cloud software, small businesses get access to always up-to-date versions of applications without having to manually update them. The service provider ensures that all systems are constantly updated, providing not only access to the latest features, but also security patches and bug fixes.
Automatic updates eliminate the need to hire IT specialists to perform these operations, reduce the risk of using outdated software, and allow your team to focus on core business rather than technical issues.
*To learn more about maximizing IT productivity in your organization, check out our latest article: https://prosteit.pl/jak-przyspieszyc-firmowy-internet-i-optymalizowac-siec/
How much does cloud computing cost?
Factors influencing price
Cost of cloud services for a small business depends on many factors. The most important are:
- • Computing power requirements – number and performance of virtual processors (vCPU) and amount of RAM
- • Data storage capacity – amount of disk space needed and type of storage (SSD, HDD)
- • Data transfer – amount of data transferred to and from the cloud
- • Complexity of infrastructure – number of servers, services and additional tools
- • Level of security and technical support – additional security, backups, SLAs (Service Level Agreements)
- • Settlement model – pay-as-you-go, monthly subscription, long-term reservations
The choice of specific services also has a significant impact on the final price. For example, using ready-made managed services (such as databases as a service) is usually more expensive than setting up virtual servers yourself, but it requires less technical knowledge and takes less time.
Example costs of cloud solutions
Cloud service prices can range from several dozen zlotys to several thousand zlotys per month, depending on the needs and scale of the company's operations.
For a small business that needs basic infrastructure to host a website and a few business applications, the monthly cost can start at around PLN 100-300. For example, a simple virtual server with 2 CPU cores, 4 GB of RAM, and 50 GB of disk space costs around PLN 80-150 per month with most providers.
For more advanced needs, such as hosting e-commerce applications with high traffic, CRM systems or analytical platforms, costs can increase to PLN 500-2000 per month. Companies requiring high availability, advanced security and high computing power must expect to spend several thousand złoty per month.
It is also worth considering that many providers offer starter packages for small businesses, often with a free trial period or significant discounts for the first year of service.
How to optimize your cloud services spending
Despite the cloud’s pricing flexibility, costs can mount quickly without proper management. Here are some strategies to optimize your spending:
- • Matching resources to actual needs – Many providers allow you to monitor resource usage and adjust it in real time. It is worth analyzing this data regularly and reducing unused resources.
- • Using Elastic Instances – Autoscaling services automatically increase or decrease resources depending on the current load, helping you avoid paying for unused computing power.
- • Choosing the right pricing model – for fixed, predictable loads, long-term reservations are more advantageous, as they offer significant discounts compared to the pay-as-you-go model.
- • Cost analysis and monitoring – most cloud providers offer tools to analyze spending and identify areas for optimization. Regular reviews can help identify unnecessary services or suboptimal configurations.
- • Using less expensive regions – Cloud prices can vary based on data center locations. If there are no regulatory or latency concerns, it’s worth considering cheaper regions.

When is it worth implementing cloud computing in a small company?
Where the cloud brings the greatest benefits
Cloud computing is not a universal solution for every company, but in certain situations it can bring unique benefits:
- • Dynamic development of the company – if the company is growing rapidly and it is difficult to predict future demand for IT resources, the flexibility of the cloud allows you to adapt to changing needs without the risk of overinvestment.
- • Remote work or distributed teams – for companies with employees working from different locations, the cloud provides uniform access to tools and data regardless of the place of work.
- • Limited IT budget – the cloud helps startups and small businesses avoid large initial investments in infrastructure, allowing them to redirect capital to the development of their core business.
- • Seasonality of business – for companies with variable loads (e.g. e-commerce during the holiday season), the cloud enables flexible scaling of resources during periods of increased traffic.
- • The need for rapid implementation of new solutions – the cloud significantly shortens the time needed to launch new applications or services, enabling faster response to market needs.
The process of implementing cloud solutions
A well-thought-out cloud computing implementation in a small business should include the following steps:
- Needs analysis and goal setting – defining which business processes are to be supported by the cloud and what benefits the company expects.
- Choosing the right model and supplier – comparison of offers from different suppliers in terms of functionality, cost, security and technical support.
- Developing a migration strategy – deciding which applications and data to migrate to the cloud first and choosing the appropriate approach (complete or gradual migration).
- Preparing the organization – training employees and adapting internal processes to work with cloud solutions.
- Implementation and testing – transfer of selected applications and data to the cloud environment and thorough testing before full launch.
- Continuous optimization – regularly monitoring performance and costs and adapting configurations to changing business needs.
Small businesses that lack in-house IT skills may want to consider using the services of companies that specialize in cloud migration. Such IT outsourcing can speed up the implementation process and reduce the risk of errors.
Examples of applications in various industries
Cloud computing has applications in almost every industry, but here are some examples that are particularly beneficial for small businesses:
- • Retail and e-commerce – cloud solutions enable flexible scaling during periods of high traffic (e.g. Black Friday), ensure fast page loading and support customer data analytics.
- • Professional services (accounting, consulting, legal) – the cloud provides secure access to client documents from anywhere, facilitates team collaboration and automates everyday administrative tasks.
- • Production and logistics – cloud applications support supply chain management, real-time inventory monitoring and production process optimization.
- • Healthcare – the cloud enables secure storage of patient data, telemedicine and efficient management of visit schedules.
- • Education and training – cloud-based e-learning platforms enable online training, collaboration between students and teachers, and access to educational materials from any device.
Cloud FAQs for Small Businesses
Professional cloud services usually offer a higher level of security than on-premise solutions in small businesses. Providers invest in advanced security, redundant systems, and certified data centers. However, security is a shared responsibility – the provider secures the infrastructure, but the customer must take care of secure passwords, proper access management, and proper configuration.
The migration process depends on the type and amount of data, but typical approaches include:
- • "Lift and shift" migration - transfer of the application in an unchanged form
- • Refactoring – adapting the application to the cloud environment
- • Stepwise migration – transferring data and applications in batches
Most vendors offer migration tools and technical support during the process. For small businesses with no IT experience, it may be a wise option to hire outside specialists.
One of the advantages of the cloud is the ability to reduce the need for internal IT specialists. Basic operation of most cloud solutions for small businesses does not require advanced technical knowledge. Intuitive administrator interfaces allow for management of services without specialist training.
For more complex implementations or if you have specific requirements, it may be necessary to use external consultants or companies specializing in cloud services.
Switching cloud providers can be a challenge, especially if your company is using proprietary, vendor-specific services. That’s why it’s worth thinking about potential “portability” from the start and choosing standards-based solutions that will make it easier to migrate in the future.
Some companies choose to pursue a multi-cloud strategy, using multiple vendors at the same time, which reduces the risk of vendor lock-in but can increase management complexity.
Cloud computing provides small businesses with access to modern technologies without the need for large upfront investments. It offers flexibility, scalability, and potential savings that were previously unavailable to smaller entities..
Cloud services for small businesses can start at a few dozen złoty per month and grow depending on requirements. The key to optimizing expenses is to precisely match resources to actual needs and regularly monitor usage.
The decision to implement the cloud should be preceded by a thorough analysis of the company's needs, a comparison of available offers and the development of a migration strategy. It is also worth remembering that the cloud is not an ideal solution for every scenario - in some cases, the traditional approach may be more appropriate.
To sum up, cloud computing is a technology that can significantly support the development of small businesses, increase their competitiveness and facilitate adaptation to changing market conditions. Properly implemented, it is an investment in the future of the company, enabling faster response to customer needs and more effective management of IT resources.





