Imagine a key program crashing in the middle of the workday, a server failing, and employees asking when they'll be able to work normally again. Instead of waiting for an IT technician to arrive, a few minutes later someone from a trusted IT department accesses the company computer, diagnoses the problem, and restores the system—without an on-site visit or unnecessary downtime. It sounds ideal, but the natural question is: is it really safe?
Remote IT support has become standard in companies – from one-person businesses to teams dispersed across the country. Thanks to tools such as AnyDesk and similar solutions can connect to your computers and servers from virtually anywhere in Poland. However, this same mechanism is used by scammers posing as banks, software providers, or "security companies." It's not the technology itself that poses the threat, but the way it's used.
From the perspective of the management board or company owner the stakes are high: customer data, accounting system, email, banking access, brand reputation. One careless "remote assistance" session can end much worse than a printer failure. On the other hand, a well-organized online IT support is one of the most effective ways to quickly extinguish fires and keep systems running.
In this article we will show you how remote IT support really works, where the safe cooperation with an IT company ends and the risk of fraud begins, and what safety standards It's worth enforcing this from your technology partner. The goal is for you to know exactly when you can safely use such a solution and when to immediately say "stop." In other words, how to organize it in your company secure remote IT assistance.

How remote assistance works in practice (using AnyDesk and similar tools as an example)
Before you assess whether remote IT support is safe, it is important to understand, what's really going on "under the hood"“ such a connection. Tools such as AnyDesk, TeamViewer, ISL Online, ConnectWise Control Whether Splashtop they work on a very similar principle: they create temporary, encrypted tunnel between the user's computer and the IT technician. This is not "open computer access," but a carefully controlled session with clearly defined rules.
Below you'll find a detailed, yet accessible explanation of how it works, why these programs are secure, and what features protect your business from unauthorized access.
1.1. What is needed to enable remote assistance?
For an IT professional to connect to your computer, only three elements are usually needed:
Internet access
A stable connection allows you to maintain your session, although it doesn't have to be fast. These types of programs primarily transmit screen images, so they work even with average Wi-Fi.A small client program (e.g. AnyDesk, TeamViewer or QuickSupport)
It's a small application that you run once. It doesn't require installation, doesn't change your computer's settings, and doesn't run in the background after your session ends.User informed consent
No specialist can "enter" your computer without your confirmation.
Each connection requires the following:• Device ID/Address,
• One-time codes or manual acceptance of the connection.
This means that Remote support only works when you allow it. This is the first and fundamental element of safety.
1.2. What does the connection process look like step by step?
All popular tools work similarly:
You run the client program (e.g. AnyDesk, TeamViewer).
The program generates a unique identifier (ID).
You only give it to the person in the IT department you are talking to and whom you know.
The technician sends a connection request to your device.
You have to make this request consciously accept.
The technician can see your screen and perform actions you allow them to perform (more on permission levels in a moment).
You can at any time end your session with one click.
The user has full control over whether the session works and how long it lasts.
1.3. Encryption – the foundation of security in remote assistance
It is worth emphasizing one thing: programs like AnyDesk are not dangerous in themselves. Their reputation has been damaged primarily by fraudsters who attempt to exploit user trust. Technically, these solutions are highly secure.
The most important mechanisms:
• Encryption TLS 1.2/1.3
This is the same standard of protection used by banks. It means that traffic between you and your IT specialist is protected from eavesdropping.• Encryption end-to-end (E2E)
In many tools, images and data don't pass through any central server in readable form. Only your computer and the technician's computer can see them.• Encryption keys RSA 2048 / 4096
This is a verification mechanism that you're connecting with the right person, not someone impersonating an IT company. They can't be "guessed" or intercepted.• Random call codes and one-time tokens
Even if someone knew your ID, they would be unable to do anything without the one-time code.
What does this mean for the user?
• No one will be able to see your screen image during the session.
• The call cannot be "taken over".
• The technician cannot connect without your knowledge.
1.4. Permissions – the user decides what the IT specialist can do
This is one of the lesser-known but crucial security features.
In programs like AnyDesk, TeamViewer, RustDesk or Splashtop you can control:
• Is the technician can only watch the screen, or also control the mouse and keyboard.
• Can it transfer files?.
• Can it restart the computer?.
• Can it perform administrative operations?.
• Does it have access to the system clipboard (copy-paste).
In practice, this means you can set up remote assistance to:
• technician he just told you what to click,
• or performed activities for you, but only in selected areas.
This is important because some companies decide that, for example,. file transfers are always disabled, and only selected people in the IT team have administrative access.
1.5. Technician Identity Verification – Key to Eliminating the Risk of Fraud
The best tools also allow you to confirm that the technician calling you is exactly who they should be.
Standard features include:
• Trusted device lists – calls from others are automatically blocked.
• Permanent IDs for IT employees – e.g. each technician has his own certificate.
• "Only connections from authorized accounts" settings„ – no one else will start the session.
• Notifications and logs – you can check who connected to your computer and when.
This means that if your IT partner uses such features (and we do by default), it virtually eliminates the possibility of a random person initiating the call.
1.6. Installation Levels – One-Time Customer vs. Permanent Agent
This is an aspect that often causes misunderstandings, and it is good to clarify it.
1) One-time connection (QuickSupport / Portable)
• Used for short reports, minor problems, individual employees.
• No installation, no background access.
• Once you close the browser or program, access disappears.
This is the safest form for the user because the technician has no access outside the session.
2) Permanent agent (installed on the computer/server)
• Used mainly in companies that have signed a permanent IT service contract.
• It allows the IT specialist to connect even when the user is not sitting at the computer (e.g. servers, warehouse equipment, reception computers).
• Access is protected by passwords, keys, a list of trusted devices, and sessions are logged.
For management boards it is important to: a permanent agent does not provide unlimited control. Access is filtered by permissions and requires IT authorization.
1.7. Visibility of technician's activities – full transparency
Every action performed remotely is visible to the user:
• you see mouse movements,
• you see programs opening,
• you can end the call with one button.
This is different from remote vulnerabilities or backdoors, which these tools have nothing to do with.
In well-managed technical support says what he does and why.
This is important information for management boards: transparency of operations is an element of the standard of professional IT services.
1.8. Is remote assistance safe? Yes, if used properly.
The technology itself (AnyDesk, TeamViewer, Splashtop, RustDesk, etc.) is there very well secured. Risks only appear in two cases:
The scammer pretends to be an IT company and asks to connect.
The company has no procedures and does not educate employees.
Therefore, in the following chapters we will show:
• how to recognize a fake contact,
• how to organize clear rules for receiving remote assistance in the company,
• what security standards should an IT company meet so that you can fully trust it.

Where the Risks Lurk: The Most Common Remote Assistance Scam Scenarios
The biggest threat is not the remote assistance tool itself, but a fraudster posing as an IT specialist. Programs like AnyDesk and TeamViewer are technically safe – the risk arises when a user grants access to the wrong person. Below are three of the most common scenarios that will help you quickly understand what the problem is.
Fake contact from the bank
A "security specialist" calls the company, reporting alleged suspicious transactions. Under the pretext of "stopping a transfer," they request the activation of a remote access tool and the provision of an ID. The fraudster operates under time pressure and the authority of the institution, which may prevent some employees from verifying the connection. As a result, the criminal gains the ability to view the screen and manipulate the user.
Software vendor impersonation
An employee receives a call from a supposed Microsoft consultant or ERP system manufacturer. The "technician" informs them of a licensing error or security threat and offers a brief remote diagnosis. They sound professional, know the system's name, and can use technical language. Once connected, they can install malware or compromise company data. This attack works because it mimics real communication with the technology provider.
Fake email from a known contractor
The accountant receives a message from an address that looks remarkably similar to a regular partner of the company. The message reads: "The invoice is not opening correctly, please quickly check it remotely." Attached are instructions for downloading the program and a request for an ID. This is classic spear phishing – it looks credible because it's tailored to the company's daily processes.
Key takeaways for businesses
Technology is not the problem – remote assistance tools are well secured. The risk arises from misidentification people on the other side.
Scammers always:
• initiate contact,
• they use time pressure or authority,
• they ask for a quick connection,
• present an „urgent”, emotional reason.
Professional IT support Never does not cause any rush, and the process is clear and predictable.
In the next chapter we will show you what it should look like secure remote assistance standard, which protects the company against each of the above scenarios.
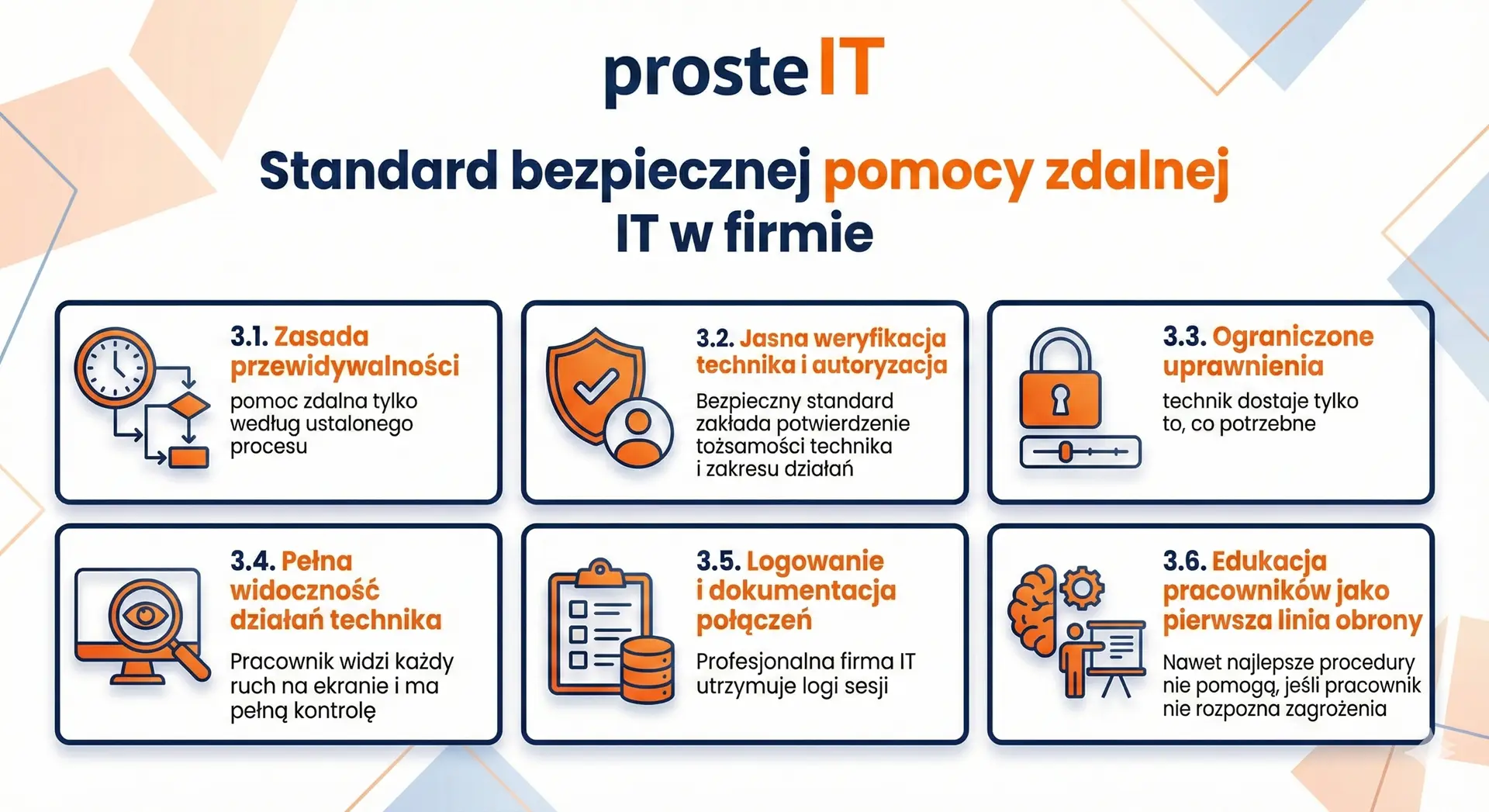
The standard for secure remote IT support in the company
Secure remote assistance isn't just about the tool itself. The foundation is clear procedures, controlled authorizations and a predictable way of working. This way, the company knows exactly what to expect from its IT partner, and employees don't have to guess whether the connection is legitimate.
Below are the most important elements of a professional safety standard.
The principle of predictability – remote assistance only according to the established process
Professional IT company never contacts by surprise, doesn't exert pressure or demand a "right away" connection. Reporting always occurs through established channels: ticketing, email, phone, or instant messaging. The employee knows they're the one initiating contact or confirming a specific report.
This eliminates most attempts to impersonate specialists.
Clear technician verification and authorization
A secure standard assumes that before a technician connects to a computer, the employee confirms:
• who is the technician (name, request number, contact channel),
• what the report concerns,
• what activities will be performed.
The connection is always there consciously accepted. If anything is questionable, the session will not start.
Limited permissions – the technician only gets what is needed
Good practices assume the use of a minimum level of permissions:
• just a screen preview if enough,
• mouse/keyboard control only when needed,
• file transfer disabled if not required,
• no access to system functions that do not apply to the report.
This approach reduces the risk of accidental changes to the system and protects sensitive data.
Full visibility of technician activities
The employee sees every movement on the screen. The technician clearly communicates:
• what does he do,
• why is he doing this,
• what will be the next step.
You can at any time stop the session with one click, giving the user complete control. Transparency is the best way to build trust.
Logging and call documentation
A professional IT company maintains session logs—who connected to a device, when, and for what purpose. If necessary, the connection history can be replayed. This is an important element of protecting business liability and compliance with security policies.
Employee education as the first line of defense
Even the best procedures won't help if an employee fails to recognize the threat. Therefore, as part of IT support, it's worth providing:
• a short instruction on what proper remote assistance looks like,
• a list of red flags (e.g. time pressure, unknown technician, strange connection reasons),
• clear rule: do not call anyone who has asked you to call them.
Companies that regularly educate their teams virtually eliminate the risk of successful fraud.
The standard for secure remote support is a combination of technology and best practices. When both elements work together, remote support becomes fast, predictable, and above all, secure. In the next chapter, we'll describe what this process looks like in our daily work with business clients.
How we organize safe remote assistance for companies
Collaborating with an IT department should provide a company with a sense of security, predictability, and peace of mind. Therefore, our approach to remote support is based on three foundations: transparency, client-side control and clear rules of work, that protect both data and business processes. We don't expect trust "just by word of mouth"—we build it with standards that are understandable even to non-technical users.
Each session begins with verification and reporting
We never call "out of the blue." Remote assistance always comes from:
• notifications in the system,
• contact by e-mail or telephone,
• conversations on a well-known messenger (Teams, WhatsApp).
This ensures the employee knows they're speaking with the right technician, understands the issue, and can make an informed decision about granting access. This eliminates situations where someone impersonates the IT company under the pretext of an urgent emergency.
Full customer control at every stage
A session can only be started with the user's consent. Technician:
• informs what he will do,
• describes the next steps,
• does not perform activities that the client does not understand or accept.
This partnership approach is crucial for us. IT support It shouldn't happen "behind the user's back." Clear communication ensures remote assistance isn't stressful and is conducted in a predictable and safe manner.
Limited and precisely controlled permissions
We apply the principle of least privilege to every call. This means the technician only has access to those areas necessary to resolve the issue. We typically disable:
• file transfer,
• administrative access,
• system operations not resulting from the report.
In practice, this limits the possibility of accidental errors and protects systems that should not be modified during rapid support.
Transparency of actions – you see everything we do
Remote support is never hidden. Users see:
• every mouse movement,
• each time you open the application,
• each diagnostic step.
If anything raises any concerns, the session can be terminated immediately with a single click. This transparency is one of the reasons why many clients treat us not as an external contractor, but as a trusted technology partner.
Login, Documentation and Responsibility
Each connection is logged. We know who connected to a given device, when, and for what purpose. This allows us to:
• maintaining full compliance with security policies,
• quick tracing of the history of activities,
• ensuring consistency between the support provided and the report.
This ensures transparent communication and clearly defined responsibilities – just as management boards and business owners expect.
A partnership approach – we support, we do not impose
We know that not everyone needs to be an IT expert. That's why our work style is simple, explanatory, and based on dialogue rather than technical monologue. We explain why we're taking specific steps, suggest best practices, and ensure the employee feels confident during the session.
Trust in the IT department is built when the customer knows exactly what is happening – and feels like they are part of the process, not a spectator.
If you want your company's remote support and IT services to be truly secure, predictable, and based on a partnership approach, we can provide you with remote support that builds trust and eliminates chaos.

How to prepare your company for safe remote assistance
Secure remote assistance starts not with tools, but with well-set internal rules. They protect employees from making poor decisions and the company from the consequences of successfully impersonating an IT specialist. Below are the most important elements worth implementing in every organization.
Clear procedures for contacting the IT department
Every employee should know:
• how to report a problem (reporting system, email, telephone),
• who from the IT company can contact him,
• in what situations a technician can request remote assistance.
This makes suspicious connection requests immediately easy to recognize.
Rule: the employee initiates or confirms the report
The most important safety rule: No one should connect to a computer unless the employee has reported the problem or confirmed the report through an official channel.
This effectively neutralizes fake „urgent breakdown” calls.
Minimum permissions and access separation
Determine that by default:
• the technician only receives basic access (e.g. screen preview),
• higher permissions require the consent of a supervisor or administrator,
• File transfers and administrative operations are performed only when necessary.
Such restrictions significantly reduce the effects of possible errors.
Brief safety instructions for employees
A simple one-page spreadsheet or PDF can make a huge impact. It should include:
• what a proper session looks like,
• what warning signals should interrupt the connection,
• what technician Never should not ask (bank details, SMS codes, financial logins).
Regular reminders build habits, not fear.
Annual review of procedures and tools
Technology and threats are changing. It's worth reviewing once a year:
• are the tools up to date,
• whether the list of authorized contact persons is correct,
• are the processes understandable to new employees,
• whether administrative access is not redundant.
This is a simple way to maintain a high level of security without unnecessary formalism.
Frequently asked questions about remote assistance
We always confirm the request through an official channel: email, ticketing system, phone, or the messaging app your company uses. The technician introduces themselves, addresses the specific request, and clearly explains the steps they will take. If the contact appears out of nowhere, it's a sign to decline the call.
Yes, provided the session is consciously accepted and conducted in accordance with security procedures. Remote support tools use bank-grade encryption, and the technician is only granted the necessary permissions to resolve the issue. Transparency protects data from unauthorized access.
Disconnect with a single click and contact your supervisor or IT administrator. A professional IT company will never begrudge you for interrupting a session—security trumps speed. If a technician insists on continuing despite your doubts, it's an additional warning sign.
Yes, we provide comprehensive remote IT support. We typically respond within 10-15 minutes, and even faster in urgent situations. The process is simple: submit a request, verify a technician, and connect immediately, so technical issues are resolved without waiting for an on-site visit.
We serve businesses locally and remotely throughout Poland. We support businesses in Warsaw, Ożarów Mazowiecki, Pruszków, Błonie, Łomianki, Janki, and the surrounding areas, among others. Remote assistance allows us to respond equally quickly regardless of the company's location.
Safe remote IT assistance it is not a matter of trust in the technology itself, but in procedures, transparency and way of working IT partner. Tools like AnyDesk, TeamViewer, and Splashtop are robustly secured – it's human decisions, lack of verification, or haste that open the door to abuse. When a company has clear rules and technicians work transparently and respect user privileges, remote support becomes not only secure but also exceptionally effective.
A well-implemented remote support standard shortens response times, reduces downtime, and ensures the continuity of work for the entire team. These are precisely the elements that are crucial to the smooth operation of a company.
If you want remote assistance and IT support in your organization to operate in a predictable, secure and fully professional manner, we can provide you with remote support that truly relieves the burden on your team and protects your company on a daily basis.