Everyone who uses cloud services in their company sooner or later asks themselves the same question: Is the data of my employees and customers really safe there? This is natural – after all, we store virtually everything these days in Microsoft 365: contracts, payroll, client correspondence, financial reports, and even team meeting recordings. For many companies, the loss or leak of such information would mean a serious crisis.
The question of Microsoft 365 security is not just about technology – it is about trust. Trust in the cloud, in configuration, and ultimately in your own company practices. Because contrary to what is often believed, Microsoft 365 itself does not guarantee 100% security. However, it guarantees powerful toolswhich, if properly implemented and managed, provide a level of protection that classic on-premise solutions can only dream of.
It is also worth knowing that even the world's largest organizations, including Fortune 500 companies, have relied on Microsoft services for years—both for teamwork and security. Microsoft 365 is not an experiment, but a business standard that has passed the most stringent security tests on the market.
But… the platform itself is only half the story. The other half is what will you do with it – how you set up access, how you respond to alerts, how you train your team. Because in practice, it's not Microsoft, but you (or your IT department) who decides who has access to what, whether data is encrypted with a corporate key, and whether passwords are protected with multi-factor authentication (MFA). And it's this part that determines the answer to the question: "Is Microsoft 365 secure in my company?"
In this article we will show full pictureFrom how Microsoft encrypts data and protects servers, to the practical differences between services (e.g., SharePoint vs. OneDrive, Teams vs. Zoom, or Exchange Online vs. email hosting with providers like home.pl or nazwa.pl). We'll also compare Microsoft Defender with other popular antiviruses, so you can see where the line really lies between "secure" and "professionally secured."
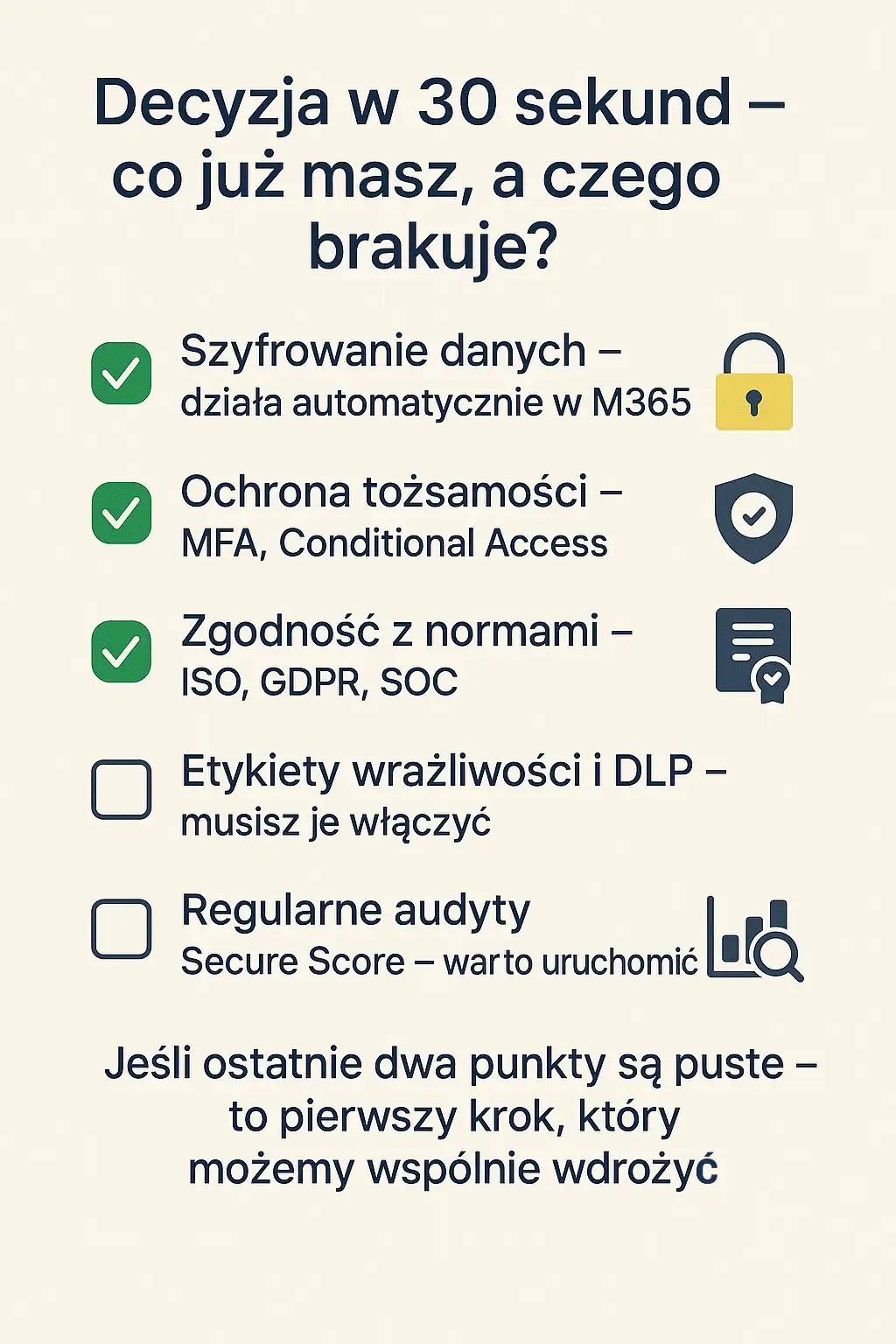
- Do all employees have MFA enabled?
- Is data encrypted and covered by DLP rules?
- Do you regularly check your Secure Score in the Microsoft 365 portal?

Is Microsoft 365 Secure? The Foundations of Cloud Data Protection
When asked whether Microsoft 365 is secure, cannot be answered in one sentence. To understand this, it is worth knowing the basics security mechanismsthat power the Microsoft cloud. It's these technologies that ensure the M365 environment meets the requirements of even the most demanding industries – from finance to public administration.
Shared Responsibility Model
One of the most overlooked, yet crucial aspects of cloud security is shared responsibility model. In short: Microsoft secures infrastructure, and You are responsible for configuration and use..
• Microsoft guarantees the physical security of data centers, service availability, data encryption, attack resistance and compliance with standards (ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR).
• Your company is responsible for who has access to data, how strong passwords are, whether multi-factor authentication (MFA) is working, and whether data is properly classified (e.g., through sensitivity labels and DLP policies).
This division is logical – the manufacturer does not know the structure of your company, so you decide how deeply you want to protect your information.
The 50/50 Rule - Microsoft is responsible for what's under the hood—servers, encryption, accessibility. You're responsible for what's inside—accounts, permissions, settings, security policies.
Data encryption – or how Microsoft “locks” your files
Microsoft 365 encrypts data both at rest and in transitIn practice, this means that even if someone intercepts network traffic or gains physical access to the server, they won't be able to read the data without the keys.
• Data on disks are secured with technology BitLocker (full disk encryption) and per-file encryption – each file has its own unique AES-256 key.
• During transmission (e.g. sending an email, sharing a file, chatting in Teams), data is encrypted using protocols TLS 1.2+ and Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP).
• For companies that want to have full control over their keys, there is an option Customer Key – allows you to use your own encryption keys, managed by your organization.
Identity and Login – The First Line of Defense
The biggest risk in the cloud world is not hacking into server rooms, but user account takeovers.
That's why Microsoft 365 bases its protection on identity management in service Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory).
Key mechanisms:
• Multi-factor authentication (MFA) – requires a second confirmation (SMS, app, physical key).
• Conditional Access – allows you to restrict logins based on device, location or risk level.
• Passwordless Sign-In – login without passwords, using biometrics or a security key (e.g. YubiKey).
• Identity Protection – behavior analysis and anomaly detection (e.g. logging in from another country at 3:00 a.m.).
Thanks to these features Microsoft 365 automatically responds to unusual behavior – may, for example, force re-authentication, block access or inform the administrator about a potential risk.
Certifications and compliance
Security is not only about technology, but also compliance with laws and industry standards.
Microsoft 365 meets the most important standards, including:
• ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 27018 (protection of personal data in the cloud)
• SOC 1, 2, 3, FedRAMP High, GDPR
• For European customers: EU Data Boundary – EU user data is stored within the EU.
These certifications are publicly available on the portal Microsoft Service Trust – it is a database where every organization can check, where the data is stored and what security measures are in place.
Data availability and redundancy
Every file stored in Microsoft 365 is automatically replicated in several data centers, often hundreds of kilometers apart.
Thanks to this, even a failure of the entire facility does not cause data loss or interruption in work.
In practice, this means:
• 99.9% Service Availability Guarantee (SLA)
• georedundancy – backups in multiple locations
• automatic traffic switching in the event of a failure
This level of reliability cannot be achieved in a classic local environment without huge investments.
Why These Fundamentals Matter for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Many SME owners assume that such advanced mechanisms are "for corporations." However, Microsoft 365 offers the exact same protection standards—regardless of whether the company has 5 or 5,000 employees. This is a huge advantage: small businesses benefit enterprise-class infrastructure without the need to build your own server rooms or security systems.
Microsoft 365 isn't "just a cloud"—it's a comprehensive security ecosystem that combines technology, compliance, and automated risk analysis. A secure Microsoft 365 isn't a marketing promise, but specific processes, encryption and access controlthat run in the background – provided that the company consciously uses them.
Is SharePoint Secure? A Comparison with OneDrive in the Enterprise
SharePoint and OneDrive are the two most frequently confused components of Microsoft 365. Both are used for file storage, both offer syncing and sharing, but they have completely different applications and levels of controlUnderstanding the difference between them is the first step to secure document management in your company.
SharePoint and OneDrive – same cloud, different goals
Contrary to appearances, SharePoint and OneDrive share the same infrastructure and the same encryption mechanisms. However, they differ the context in which they store data:
• OneDrive for Business - this user's private spaceEach employee has their own cloud storage space for work files, notes, personal documents, or drafts of materials.
• SharePoint Online - this shared space for teams, departments or projects. Enables versioning, access control, workflows, and compliance rules.
So if you ask where to keep contracts, invoices or marketing plans, the answer is: in SharePoint, not in OneDrive.
Widget: When to use SharePoint and when to use OneDrive?
• OneDrive – working files, sketches, notes, private materials.
• SharePoint – shared resources, team documents, company archives, procedures.
This will help you avoid situations where key data disappears after an employee leaves.
Data encryption and security in SharePoint and OneDrive
Technically, both solutions are identical security level:
• Encryption at rest: each file is encrypted unique AES-256 key, and the entire database is protected by BitLocker.
• Encryption in transit: data is sent only after TLS 1.2+ – regardless of whether you open the file from a browser, Teams or mobile app.
• Data isolation (tenant isolation): Each Microsoft 365 client has a dedicated environment – data from one company cannot physically or logically "penetrate" to another.
• Ransomware protection: The "Restore your OneDrive" feature allows you to revert all your files to a point before the infection or error occurred.
Thanks to this the level of data security in SharePoint and OneDrive is the same – but the way in which a company can control this data varies.
Permissions and access control – the advantage of SharePoint
The biggest difference between SharePoint and OneDrive is that who controls access to files.
• IN OneDrive The file is owned by the user. They decide who they want to share it with.
• IN SharePoint the owner of the resource is team or organization – and the administrator can globally set sharing rules, restrict external links, force work login or add DLP (Data Loss Prevention) rules.
In practice, this means that SharePoint is better suited for managing sensitive information – e.g., finances, HR data, project documents. OneDrive is a great tool for individual work, but it won't replace the control structure provided by SharePoint.
Data versioning and recovery
Each file in SharePoint and OneDrive has its own change history – the so-called versioning.
By default, even 500 versions a given document, which allows you to restore a previous state at any time.
Additionally, both systems have two-stage basket – first the user, then the administrator – so accidental deletions can be undone even after several weeks.
The most common user errors
Store shared documents in OneDrive instead of SharePoint.
Share files with the "anyone with link" link without restrictions.
No sensitivity labels – no file-level encryption.
Lack of versioning – users turn it off for fear of “clutter”.
All of these problems can be easily resolved with a few simple adjustments – often within a day.
File Sharing and External Security
Microsoft 365 gives you full control over what who and how may share data outside the company.
In SharePoint and OneDrive, the administrator can specify:
• Do external users need to log in with a Microsoft account?
• whether links can only work for a certain period of time,
• can you download files or just view them online,
• whether data can be sent via Teams or email outside the organization.
This is where the advantage of SharePoint comes in – it allows you to create policies at the level of entire sites, teams or groups.
This saves you from having to manually configure each folder, like in OneDrive.
Why SharePoint is more secure in a corporate environment
To sum up - SharePoint and OneDrive are equally technically secure, but only SharePoint gives full organizational control:
• central sharing rules,
• compliance with regulations (GDPR, ISO),
• access monitoring,
• and resistance to human errors (e.g. accidental file deletion).
That's why most companies—from small accounting firms to Fortune 500 corporations—store documents in SharePoint rather than in individual clouds. If you're looking to streamline how your company stores documents, we can help you migrate files from OneDrive to secure SharePoint and implement GDPR-compliant policies.

Is Teams Secure? How Microsoft Protects Company Meetings and Chats
Microsoft Teams has become the heart of business communication. It's where daily conversations, video meetings, and document and file exchanges take place. It's no wonder that one of the most common questions from business owners is: Is Teams secure and is it worth entrusting confidential information to it?
The answer is: yes – but only if you use them consciously.
Teams is inherently secure (through encryption, certificates, and access controls), but the ultimate level of protection depends on your organization's configuration and policies.
How Microsoft Secures Data in Teams
Every message, file, and conversation in Teams passes through layers of security:
• Encryption in transit (TLS and SRTP) – all data transferred between users, servers and devices is protected.
• Encryption at Rest (AES-256) – conversations, files, and metadata are encrypted on drives in Microsoft data centers.
• End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) – available for 1:1 connections; allows only the sender and recipient to decrypt the data.
• Authorization via Entra ID (Azure AD) – user identity control, MFA, Conditional Access.
• Data Residency (EU Data Boundary) – European users' data is stored only within the EU.
What is encrypted in Teams?
• Chat conversations and messages
• Files transferred via chat and channels
• Meeting notes, attachments, calendars
• Full E2EE only for 1:1 calls – SRTP/TLS encryption is used in group meetings
Microsoft applies the principle "security by design" – all data in Teams is encrypted automatically, without the need for user configuration.
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) – Facts and Limitations
There are many myths surrounding E2EE encryption in Teams. In practice, it looks like this:
• E2EE is only available for 1:1 connections.
To enable them in your organization, your administrator must activate a special policy.• In E2EE mode, some functions are disabled, e.g. recording, transcriptions, screen sharing and reactions.
• For group meetings, Teams uses encryption SRTP/TLS, which still prevents interception of data in network traffic.
It's important to be honest about this - E2EE is not the default mode because requires functional compromisesBut even without E2EE, data in Teams is end-to-end encrypted at the transport and disk levels, which effectively protects them against unauthorized access.
File Retention and Compliance
Many people don't realize that Teams does not store files itself.
Every file sent in a chat or channel goes to SharePoint Online (for channels) or OneDrive for Business (for private chats)This means that file security in Teams = SharePoint and OneDrive security.
This ensures that all retention, DLP (Data Loss Prevention), versioning, and file encryption policies are automatically inherited. Additionally, organizations can enable Microsoft Purview to monitor confidential content (e.g. PESEL numbers, customer data, financial documents).
How to check where your files go?
• Private chat files → folder Microsoft Teams Chat Files in OneDrive.
• Files from team channels → document library in SharePoint.
This is important because security policies (e.g. sensitivity labels) apply in these locations.
Access control and call protection
Teams is integrated with Microsoft Entra ID, which allows full control over access to chats and meetings.
Administrators can, among other things:
• force work login before joining a meeting,
• block the participation of guests from outside the organization,
• require MFA when logging in to Teams,
• determine which devices are trusted,
• log and audit all events (audit logs in Purview).
Additionally, as part of Defender for Office 365 the mechanism works Safe Links, which protects you from clicking on malicious links sent in chats or messages.
This is a unique feature – competitors like Zoom or Google Chat do not offer such deep security integration with the identity and DLP system.
Privacy and Compliance
Microsoft doesn't analyze chat content or use it for advertising purposes, unlike some free messaging services. Teams meets rigorous compliance standards, including: ISO 27001, SOC2, GDPRand the data of European users are covered by the principle EU Data Boundary. Additionally, all user actions are recorded in audit logs, which makes it easier to meet legal requirements (e.g. GDPR or ISO).

Each of these tools is safe today, but Microsoft Teams stands out for its integration – combines encryption, identity (Entra ID), link protection (Defender) and DLP policies in a single environment.
This means that even a small company can have enterprise-level security standards – without having to use several different applications.
Zoom and Google Chat offer solid protection, but require additional configurations or external systems (e.g., Vault, external DLP) to achieve a similar level of control.
Which tool should I choose?
• Teams – full integration with M365, DLP, Defender, GDPR, audit.
• Zoom – convenient meetings, but less central security control.
• Google Chat – good protection, but fewer compliance tools.
If your company uses Microsoft 365, choosing Teams is the natural, secure and most consistent solution.
If you want to make sure your Teams conversations are properly secured – from MFA policies to E2EE and DLP rules – We'll help you configure Teams so that it protects your data and doesn't hinder your work..
We will implement security policies tailored to the real needs of your company.

Is Exchange Online Secure? Compared to Corporate Email Hosting
Many business owners have become accustomed to traditional hosting solutions—like home.pl, nazwa.pl, or ovh.pl—where email is simply an "add-on" to the domain. This works—until a phishing attack, an infected attachment, or accidental sending of confidential customer data to the wrong address occurs. Then the question arises: Is it worth moving email to Exchange Online in Microsoft 365?
Why email is a critical point of company security
E-mail is today the main route of cyber attacksOver 90% of phishing and scam attempts begin with an email, and the cost of a single incident can reach tens of thousands of zlotys. That's why modern email solutions are no longer limited to "mailbox and password"—they encompass a comprehensive security system: scanning, encryption, attachment protection, and data control.
Microsoft built Exchange Online around this idea: Email is not just communication, it is a critical business resource that must be monitored and secured at every stage.
Exchange Online – How does Microsoft protect your email?
Exchange Online, part of Microsoft 365, operates within a global infrastructure built on the same security standards as Azure and Teams. Beneath it are multiple layers of protection:
1. Anti-spam and anti-phishing protection
Every email goes through Exchange Online Protection (EOP) – a system that analyzes the sender, content, and attachments. EOP uses heuristic, reputation, and machine filters. It blocks:
• spam and spoofing (impersonating the sender),
• phishing links (integration with Defender Safe Links),
• infected files (Safe Attachments scanning).
2. Message encryption
All connections are protected by TLS 1.2+, and Exchange also allows encryption of message content using Microsoft Purview Message Encryption or S/MIMEThis means that even if the message is intercepted, it cannot be read without the encryption key.
3. Sender Authentication and Reputation
Exchange Online automatically configures and enforces standards:
• SPF (Sender Policy Framework) – checks whether the server has the right to send messages on behalf of the domain,
• DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) – digitally signs messages,
• DMARC – specifies what to do with messages that do not comply with SPF/DKIM rules.
It is the lack of these mechanisms that is often the reason why emails from classic hosting providers end up in spam.
4. User safety
An additional layer of protection is MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) and Conditional Access, i.e. the ability to limit logins to company devices and locations.
5. Compliance with regulations
Exchange Online meets the requirements GDPR, ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA and EU Data Boundary – European users' data is stored exclusively in data centers within the EU.
What Exchange Online gives you (in short)
• Anti-spam and anti-phishing protection (EOP)
• Encryption of messages and attachments
• Compliance with GDPR and ISO standards
• Login Control and MFA
• Archiving, eDiscovery and Retention
• None – if you use classic email hosting
These aren't "premium extras" – they're the security standard in Microsoft 365 Business.
How does it compare with home.pl and nazwa.pl?
Many entrepreneurs choose email hosting with companies such as home.pl Whether nazwa.pl – mainly because it's cheaper and comes "included with the domain." The problem is that while both platforms provide a solid security foundation, they do not offer as extensive a set of security and auditing tools as Exchange Online.
• home.pl
• Email protected by anti-spam, anti-virus and two-factor authentication (2FA).
• Service SPF, DKIM and DMARC, but configuration often requires manual intervention.
• No advanced DLP, eDiscovery, versioning, or archiving features at the organizational level.
• No integration with MDM or Secure Score systems.
• nazwa.pl
• Modern DNSSEC and DNS-over-TLS protection (for domains),
• Two-step login verification,
• Basic spam filters and SPF/DKIM,
• Lack of mechanisms for message retention, classification and encryption at the user level.
• Lack of central auditing, reporting and integration with DLP tools.
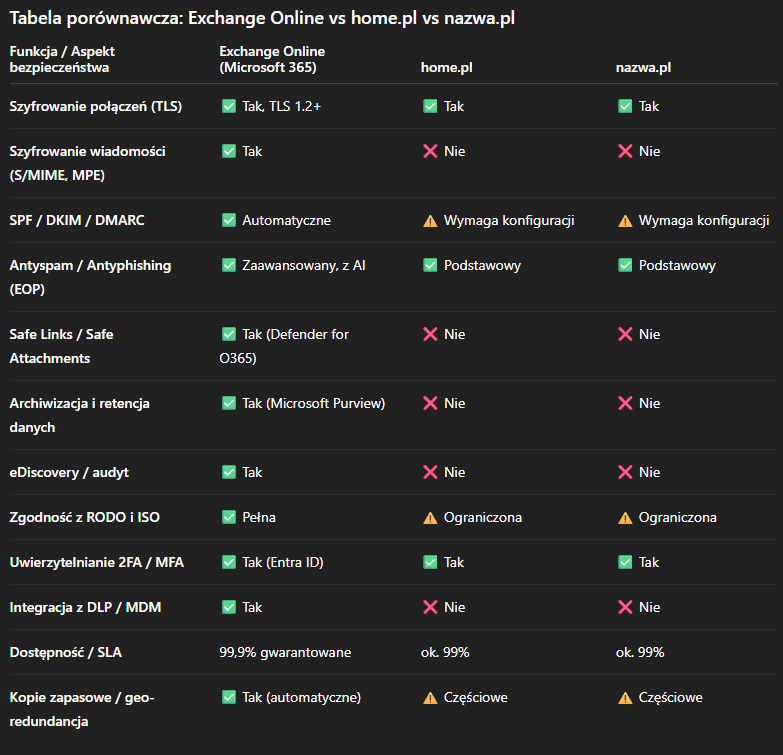
Comparison table: Exchange Online vs home.pl and nazwa.pl
Conclusions from the comparison
• Exchange Online offers a much higher level of security and compliance.
• home.pl and nazwa.pl provide a solid foundation, but lack enterprise-class mechanisms (e.g. retention, auditing, DLP).
• For companies handling customer or financial data – Exchange Online is undoubtedly the better choice.
It is also worth adding that in Exchange Online you can force automatic message encryption – for example, when PESEL numbers, invoices, or passwords are detected. This is something that traditional hosting servers simply cannot handle.
To sum up, Exchange Online It's not just email – it's a full-fledged security and compliance system where every message, attachment, and login is monitored, encrypted, and audited.
Hosted mailboxes (home.pl, nazwa.pl) work well in simple scenarios, but they do not protect business data at the level that the market requires todayIf you want to feel that your email is truly secure, it's worth taking the step towards Microsoft 365.
Microsoft Defender Security – Is it worth trusting Microsoft's protection?
Just a few years ago, many users treated Windows Defender as a "temporary protection" until they installed "real antivirus”. Today it's a completely different story. Microsoft Defender – in the company version known as Defender for Business or Defender for Endpoint – has become one of the most advanced device and data protection systems in the world.
Importantly, it's no longer just a classic antivirus. full security ecosystem, which connects:
• cloud threat analysis,
• file and email protection,
• monitoring user activity,
• and automatic incident response.
How Microsoft Defender Works – in a nutshell
Microsoft Defender uses a multi-layered protection architecture:
Real-time protection – detects and blocks malicious files, scripts and system processes.
Cloud-delivered protection – data on new threats is immediately compared with the global Microsoft Threat Intelligence database, covering hundreds of millions of devices.
Application behavior monitoring – the system learns typical behavior patterns and blocks unknown processes that behave suspiciously.
Application Control and Exploit Protection – blocks code injection and known attack techniques (e.g. exploit kits).
Document protection in M365 – thanks to integration with Defender for Office 365, all attachments and links in emails and Teams are scanned before opening.
What Microsoft Defender Protects (Business / Endpoint)
Windows, macOS, Android and iOS systems
Exchange and Teams mail
Files in SharePoint and OneDrive
Browsing (URL protection and domain reputation)
End devices – laptops, stations, servers
In practice: one administration panel that sees everything – from your computer to your email inbox.
Defender's greatest strength – integration with Microsoft 365
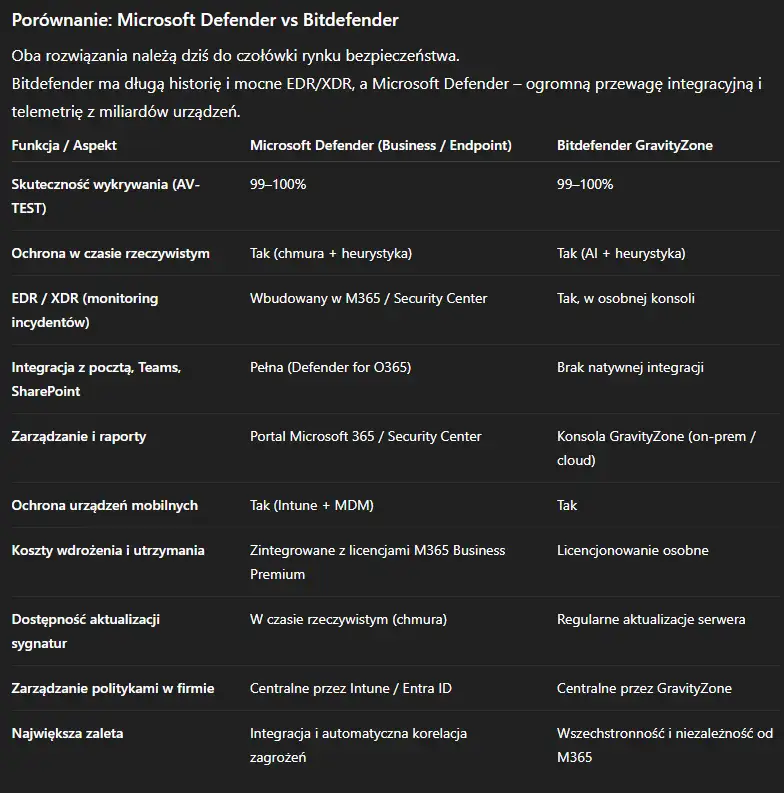
What really sets the Defender apart is its tight integration with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
This ensures that all security elements – email, files, identity, devices – exchange data in real time.
Example:
If a user clicks on a suspicious link in an email, Defender for Office 365 blocks the page, and Defender for Endpoint marks their computer as "potentially at risk" and restricts access to corporate resources. This level of automatic response is difficult to achieve in environments where antivirus runs as a standalone application.
Test Results – Facts Instead of Opinions
In tests by independent laboratories AV-TEST and AV-Comparatives Microsoft Defender has maintained its results for several years at the level of 99–100% threat detection effectivenessThis means it's on par with the best commercial antiviruses, such as Bitdefender and ESET.
• In the test AV-TEST (Enterprise, 2025) The Defender scored maximum points for protection, performance and usability.
• In the test AV-Comparatives Real-World Protection Test (2024) achieved 100% malware blocking effectiveness no false alarms.
• Microsoft is also a leader in the category endpoint detection and response (EDR) according to Gartner and Forrester reports.
Microsoft Defender and Device Management (Intune)
Defender doesn't stop at antivirus protection - it works with Microsoft Intune, which allows you to enforce security policies on devices:
• Requires disk encryption (BitLocker),
• Automatic system updates,
• Blocking the installation of unauthorized applications,
• PIN or biometrics enforcement,
• Isolation of work data (BYOD – employee private devices).
This allows the company to enforce real safety standards even in a remote work model.
Microsoft Defender is one of the most effective security solutions for businesses today – not just antivirus, but an entire device and data security management system. In independent tests, it matches the best premium products, and thanks to integration with Microsoft 365, it surpasses them in terms of consistency and automation. For most small and medium-sized businesses, this the best choice – simple, effective and always up to date.

Residency and compliance: EU Data Boundary, Multi-Geo, certifications
Data security is not only about protection against cyberattacks, but also compliance with laws and industry standardsMicrosoft 365 is designed to meet these requirements in every region of the world – including the European Union, which has one of the strictest data protection laws (GDPR).
EU Data Boundary – user data remains in the EU
From 2023, Microsoft introduced the so-called EU Data Boundary, which is the data processing boundary within the European Union. This means that European users' data (mail, files, chats, logs, metadata) are stored and processed exclusively in data centers located within the EU – including in Ireland, the Netherlands and Finland.
This policy covers the main services:
• Exchange Online,
• SharePoint and OneDrive,
• Teams,
• Entra ID (Azure AD).
Thanks to this, organizations in Poland, Germany or France have a guarantee that their data does not leave European jurisdiction, even with Microsoft's technical support.
Multi-Geo – control over data location in global companies
For organizations operating in several countries, Microsoft offers a model Multi-Geo – the ability to specify in which region of the world user or team data should be stored.
Example:
a company with branches in Poland, the US and Japan can store the data of European employees in the EU, and those of American employees in data centers in the US.
This solution is particularly useful for companies that need to comply with local data residency requirements (e.g. in the financial, legal or public sectors).
Certifications and compliance
Microsoft 365 has a wide range of certifications confirming its compliance with security and privacy standards. The most important include:
• ISO/IEC 27001 – information security management system,
• ISO/IEC 27018 – protection of personal data in the cloud,
• SOC 1, SOC 2, SOC 3 – independent audits of security processes,
• GDPR – full compliance with the European Data Protection Regulation,
• FedRAMP High / HIPAA – standards for the public and medical sectors (USA).
Microsoft publishes all certificates and audits on the website Service Trust Portal, where any company can download up-to-date compliance reports.
Why is this important for your business?
Thanks to mechanisms such as EU Data Boundary or Multi-Geo, customer data is protected not only technically, but also legally and organizationallyThis means that by using Microsoft 365, you comply with GDPR requirements and can safely store sensitive data – without the risk of it being transferred outside of Europe.
A secure Microsoft 365 starts with setup
The Microsoft 365 platform itself is extremely secure – but that doesn't mean it's each configuration is automatically safeMany companies operate with default settings that don't always protect against modern threats. That's why Microsoft and independent organizations have created tools to help assess and improve the security of their environments.
Secure Score – the first step towards a real security assessment
Microsoft Secure Score is a built-in tool that rates your organization's Microsoft 365 configuration on a scale of 0 to 100. It analyzes elements such as:
• MFA enabled,
• email configuration (SPF, DKIM, DMARC),
• device and file security,
• administrator access and sharing rules.
The result is not just a "number" - it is a specific list of recommendationsthat you can implement to increase your level of protection at no additional cost.
It's worth knowing
A Secure Score above 70 indicates good security.
Below 50 – Your environment requires urgent improvements.
CIS Standards and CISA ScuBA Guidelines
For more advanced organizations, independent cloud configuration standards have been developed:
• CIS Benchmarks (Center for Internet Security) – ready-made sets of good security practices for Microsoft 365, Exchange and Teams.
• CISA SCuBA (Secure Cloud Business Applications) – American guidelines developed by the CISA agency, which define minimum security requirements for business clouds, including Microsoft 365.
Both sets of recommendations are public and regularly updated. In practice, many points overlap with what Secure Score suggests, but they differ in detail and requirements for large organizations (e.g., retention policies, DLP, access audits).
The simplest conclusion
Microsoft 365 is only as secure as its configuration. Even the best encryption and certificates aren't enough if users have weak passwords and MFA is disabled. Therefore, regularly checking your Secure Score and implementing CIS or CISA recommendations is the easiest way to maintain real security in your daily work.
Frequently asked questions
Yes. Microsoft 365 is one of the most secure cloud platforms in the world, used by Fortune 500 companies.
Protects data through encryption, access control, threat analysis and compliance with ISO and GDPR standards.
However, proper implementation is key – it is the configuration that determines the level of protection.
Technically yes – both encrypt data with the same AES-256 mechanism.
The difference is control: SharePoint gives you full administration, DLP rules and sharing policies, while OneDrive is a user's private space.
That's why it's always better to keep company files in SharePoint.
This is highly unlikely. Teams relies on Entra ID (Azure AD) identity and TLS/SRTP encryption.
The biggest threat is not the Microsoft servers themselves, but weak passwords or lack of MFA on the user side.
Enabling multi-factor authentication effectively eliminates this risk.
In most cases, yes. Defender for Business protects not only computers but also email, files, and user accounts.
It works in real time, analyzes behavior, and integrates with the rest of Microsoft 365 services, allowing you to quickly respond to threats.
The easiest way is through Secure Score in the Microsoft 365 portal.
This free tool shows you which security measures are active and which ones you should enable.
Additionally, you can compare your configuration with the standards CIS or CISA ScuBAto ensure you meet industry best practices.
Microsoft 365 is one of the most secure cloud work environments today – used by thousands of companies, from small offices to Fortune 500 corporations. However, it's not just about technology, but also about the way it is implemented and managed.
SharePoint, Teams, Exchange, and Defender offer advanced encryption, access control, and automatic protection mechanisms, but their effectiveness depends on configuration. Tools such as Secure Score, guidelines CIS and CISA ScuBA show that security in Microsoft 365 is a process, not a one-time setting.
A well-configured M365 environment can reduce the risk of data leakage, phishing attacks, or file loss to virtually zero – and without additional costs or external applications.
If your company uses Microsoft 365 but you're not sure if the environment is secure – we'll help you verify this. We'll conduct a configuration audit, enable appropriate security measures, and ensure your data is protected as it should be.
Security doesn't happen by accident - it's built consciously.