Choosing the right drive for your business computer is a decision that affects both your productivity and your business costs. In 2025, the market will offer three main technologies: traditional SATA HDDs, faster SATA SSDs, and the latest and most efficient NVMe drives. Which of these options will work best in a business environment? Is it always worth investing in the latest technology? In this comprehensive article, we will compare all aspects of these solutions to help you make the best decision for your business.

Types of disks - HDD, SSD SATA, NVMe and their characteristics
Before we move on to detailed comparisons, it is worth understanding the differences between the various disk technologies currently available on the market.
HDD SATA Drives – The Traditional Solution
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) hard drives are the oldest of the technologies discussed, based on mechanical elements - rotating magnetic platters and a read/write head. These drives use the SATA (Serial ATA) interface, which allows for data transfer at speeds of up to 600 MB/s.
Advantages of HDD drives:
- • Low price per unit of capacity (often below PLN 0.10 per GB)
- • Availability in very large capacities (up to 20 TB)
- • Mature, proven technology
- • Good compatibility with older hardware
Disadvantages of HDD drives:
- • Slow read and write speeds compared to SSD
- • Long data access time
- • Susceptibility to mechanical damage
- • Increased energy consumption and noise generation
- • Limited service life due to moving parts
HDDs They are mainly used as data storage, archives and backups, where access speed is not crucial and what counts most is large capacity at low cost.

SATA SSDs – a compromise between performance and price
SATA SSDs (Solid State Drives) are a flash-based solution with no moving parts. Although they use the same SATA interface as HDDs, they offer much higher efficiency thanks to a different construction.Advantages of SATA SSDs:
- • Data reading and writing many times faster than HDD
- • No moving parts, which increases resistance to mechanical damage
- • Quiet operation
- • Lower energy consumption
- • Shorter data access time
Disadvantages of SATA SSDs:
- • Higher price per GB than in the case of HDD (around PLN 0.30-0.40 per GB)
- • Limited transfer speed via SATA interface (maximum around 550-600 MB/s)
- • Limited number of write cycles (although significantly improved in newer models)

NVMe Drives – The Technology of the Future
NVMe drives (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is the latest and most efficient technology. Instead of a SATA interface, they use a direct connection to the PCIe (PCI Express) bus, eliminating the bandwidth bottleneck.Advantages of NVMe drives:
- • Extremely high throughput (from 3500 MB/s to over 14000 MB/s in the latest PCIe 5.0 models)
- • Very low access latency
- • Support for multiple command queues simultaneously, which translates into better performance in multitasking environments
- • Compact form factor for mounting directly on the motherboard (M.2 connector)
- • No additional cabling required
Disadvantages of NVMe drives:
- • Highest price per GB (although the difference is decreasing, especially in basic models)
- • Compatible motherboard with M.2 slot and NVMe support required
- • Increased heat generation, especially in the highest efficiency models
- • Potentially shorter run time at full load due to thermal throttling

The most important factors when choosing a drive for your business computer
Choosing a drive for your business computer is a decision that affects performance, data security, and work comfort. Here are the key aspects to consider:
1. Disk type: HDD, SSD SATA, SSD NVMe
- • HDD (platter disk) – large capacity at a low price, but low efficiency and higher failure rate.
- • SSD SATA - significantly faster than HDD, a good compromise between price and performance.
- • SSD NVMe (M.2) – highest performance, very fast access to data, ideal for demanding tasks, but higher price.
2. Disk capacity
- • Choose the capacity that suits your company's real needs – 256–512 GB is enough for office work, while 1 TB or more is worth considering for working with large files (graphics, video).
3. Performance: Read and write speed
- • The higher the read/write speed, the faster the system and applications start and the more efficiently data is processed.
- • NVMe SSDs offer speeds many times faster than SATA SSDs and HDDs.
4. Durability and reliability
- • Parameters such as TBW (Total Bytes Written) and MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) determine how long a drive will operate without failure.
- • In a corporate environment, it is worth choosing models with higher durability, especially for intensive work or servers.
5. Computer Compatibility
- • Check if your motherboard supports the selected drive type (SATA, M.2, NVMe).
- • On older computers, you may need to limit yourself to SATA drives.
6. Price and price-performance ratio
- • Consider whether the higher performance justifies the higher cost – simple office tasks don’t always require the most expensive drive.
7. Data security
- • Consider opting for drives that support hardware encryption.
- • For archiving and backup of data, large-capacity HDDs or RAID configurations are better.
8. Manufacturer warranty and support
- • A longer warranty and good after-sales service mean greater investment security.
9. Additional features and technologies
- • Cache – a larger cache improves performance, especially for large files.
- • 24/7 operation support – important for servers and computers operating non-stop.
When choosing a drive for a company computer, pay attention to the type and capacity of the drive, performance, durability, compatibility, price, data security, warranty and additional features. A well-chosen drive means not only faster work, but also greater reliability and security of company data.
Performance in numbers - transfer and access time comparison
To better understand the differences between each type of drive, let's take a look at specific performance parameters.Read and write speeds This parameter determines how fast the disk can read and write data. Here are typical values for different types of disks:
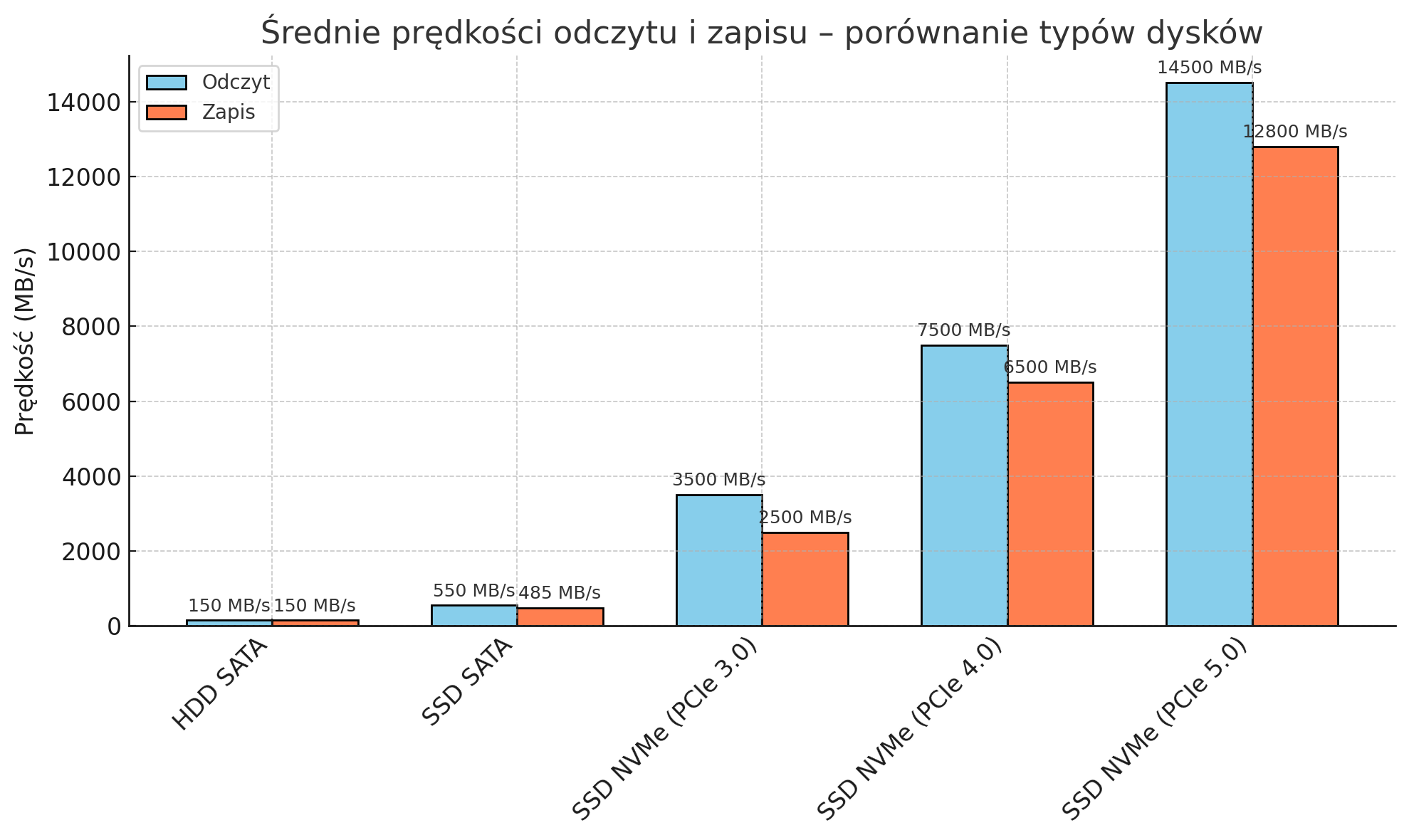
IOPS – Input/Output Operations Per Second
IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) is a measure of how many read/write operations a disk can perform in a second. This metric is especially important in multitasking and database environments.
HDD SATA:
- • Random Read/Write: 50-200 IOPS
SSD SATA:
- • Random Read: 50,000-90,000 IOPS
- • Random Write: 80,000-90,000 IOPS
NVMe SSD:
- • Random Read: 500,000-1,000,000+ IOPS
- • Random Write: 400,000-1,000,000+ IOPS
This huge difference in IOPS translates directly into the smoothness of the operating system, the speed of application launches, and the responsiveness of databases.
Research shows that using NVMe drives can improve read performance by up to 33% compared to standard SATA SSDs, especially in read-intensive environments.
Cost analysis – is it worth paying extra?
Cost is one of the most important factors when making decisions in the business environment. Let's take a look at the prices of individual solutions and whether investing in faster drives is actually worth it.Price per gigabyte – comparison 2025
Cost comparison per gigabyte (PLN/GB) based on current prices (April 2025):
SATA hard drive:
-
• Consumer drives: PLN 0.08-0.12/GB
-
• Server-class drives: PLN 0.15-0.20/GB
SATA SSD:
-
• Basic disks: PLN 0.28-0.35/GB
-
• Higher-end drives (e.g. Samsung 870 EVO): PLN 0.32-0.39/GB
NVMe SSD (PCIe 3.0):
-
• Basic models (e.g. Gigabyte Gen3): PLN 0.22-0.30/GB
-
• Mid-range model (e.g. Samsung 980): PLN 0.30-0.40/GB
NVMe SSD (PCIe 4.0):
-
• Basic models (e.g. Netac NV5000): PLN 0.24-0.32/GB
-
• Higher-end models (e.g. Sabrent Rocket 4 Plus): PLN 0.43-0.55/GB
NVMe SSD (PCIe 5.0):
-
• High-end models (e.g. Samsung 9100 PRO): PLN 0.55-0.65/GB
-
• Premium models (e.g. Gigabyte Aorus Gen5): PLN 0.65-0.75/GB
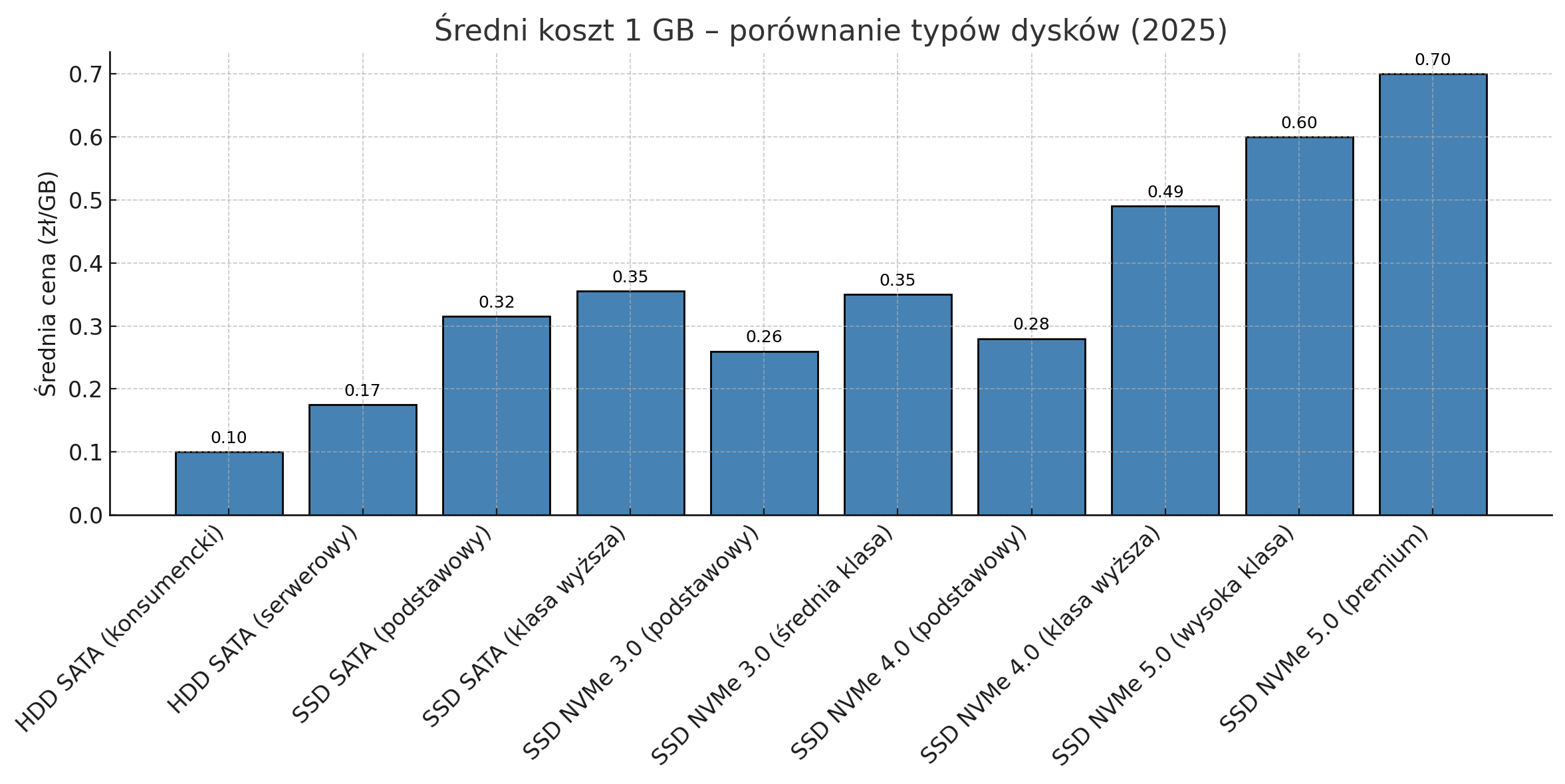
Total Cost of Ownership(TCO)
When assessing profitability, it is worth considering not only the purchase costs, but also the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes:
Energy consumption – HDD drives consume up to 3-5 times more energy than SSD drives, which translates into higher electricity bills
Cooling costs – greater heat emission by HDD affects the costs of air conditioning in server rooms
Space costs – NVMe M.2 drives take up significantly less space than 2.5″ and 3.5″ drives
Service costs – SSD and NVMe drives are more reliable than HDD, which reduces service and replacement costs
Downtime costs – a system disk failure causes downtime that costs the company money
Considering the above factors, the difference in TCO between HDD and SSD/NVMe drives can be much smaller than the purchase cost alone suggests.
Cost of business downtime
It is also worth considering how much each minute of downtime caused by a slow computer or disk failure costs the company. The average cost of an hour of downtime in a small company is estimated at hundreds of zlotys, and in medium-sized enterprises it can be even several thousand zlotys.
Let's assume that an employee earns PLN 50/h and spends 15 minutes (0.25h) a day waiting for applications, databases or access to files to load. Over a year (approximately 250 working days), this amounts to 62.5 hours, or a loss of PLN 3,125 per year - just for one employee!
Investing in a faster SATA or NVMe SSD can reduce these times by 70-90%, translating into direct savings that exceed the difference in drive price.
Business Applications – Which Drive for Which Task?
Different business environments have different drive performance requirements. Below are some recommendations for typical use cases.Workstations and office computers
For typical office use, such as working with documents, spreadsheets, browsing the internet or using email: Basic recommendation: SSD SATA 500GB or 1TB- • Provides sufficient performance for everyday tasks
- • Significant improvement over HDD at moderate cost
- • Good compromise between performance and price
- • Better system and application responsiveness
- • Start your computer and programs faster
- • Currently, prices are similar to SSD SATA with much better performance
- • Large document archive: Additional 2 TB HDD as data drive
- • Customer Service Point Computers: NVMe for maximum responsiveness
Servers and databases
For corporate servers, especially those supporting databases, virtualization or web applications: Basic recommendation: NVMe PCIe 3.0/4.0 in RAID configuration for system and applications + HDD in RAID for archive- • NVMe provides quick access to frequently used data and applications
- • HDDs in RAID arrays offer large space for archives at a lower cost
- • Maximum performance for critical business applications
- • Much higher IOPS, which is crucial for database servers
- • Ability to handle more simultaneous operations
Graphics and multimedia stations
For computers used for graphics processing, video editing, 3D rendering, and other creative applications: Basic recommendation: NVMe PCIe 4.0 1TB or 2TB- • Fast reading and writing of large multimedia files
- • Smooth work with real-time effects
- • Faster rendering and project export times
- • Maximum performance for the most demanding applications
- • Ability to work with multiple high-definition video streams simultaneously
- • Significantly reduced export and rendering times
Durability and reliability – a key aspect for companies
In a business environment, reliability is often more important than performance. Disk failure can lead to data loss, downtime, and significant financial losses.TBW – total amount of data written
TBW (Total Bytes Written) determines how much data can be written to the drive before it wears out. Typical values for 1TB consumer drives:HDD SATA:
- • No official TBW limits, but mechanical wear occurs after 3-5 years of intensive use
Consumer SATA SSD:
- • TBW: 300-600 TB
Enterprise-class SATA SSD:
- • TBW: 1000-3000 TB
Consumer NVMe:
- • TBW: 600-1200 TB
Enterprise-class NVMe:
- • TBW: 2000-5000 TB
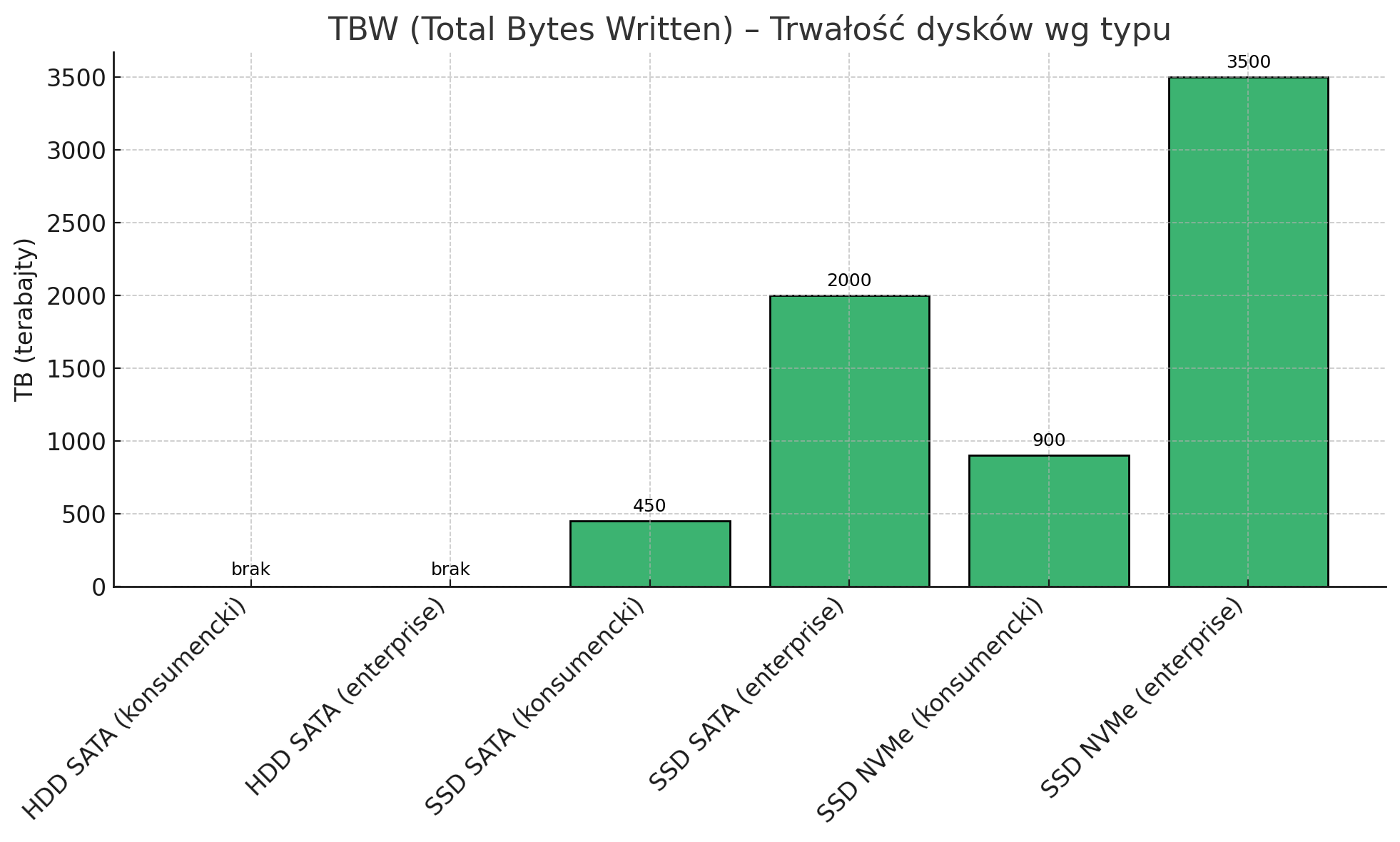
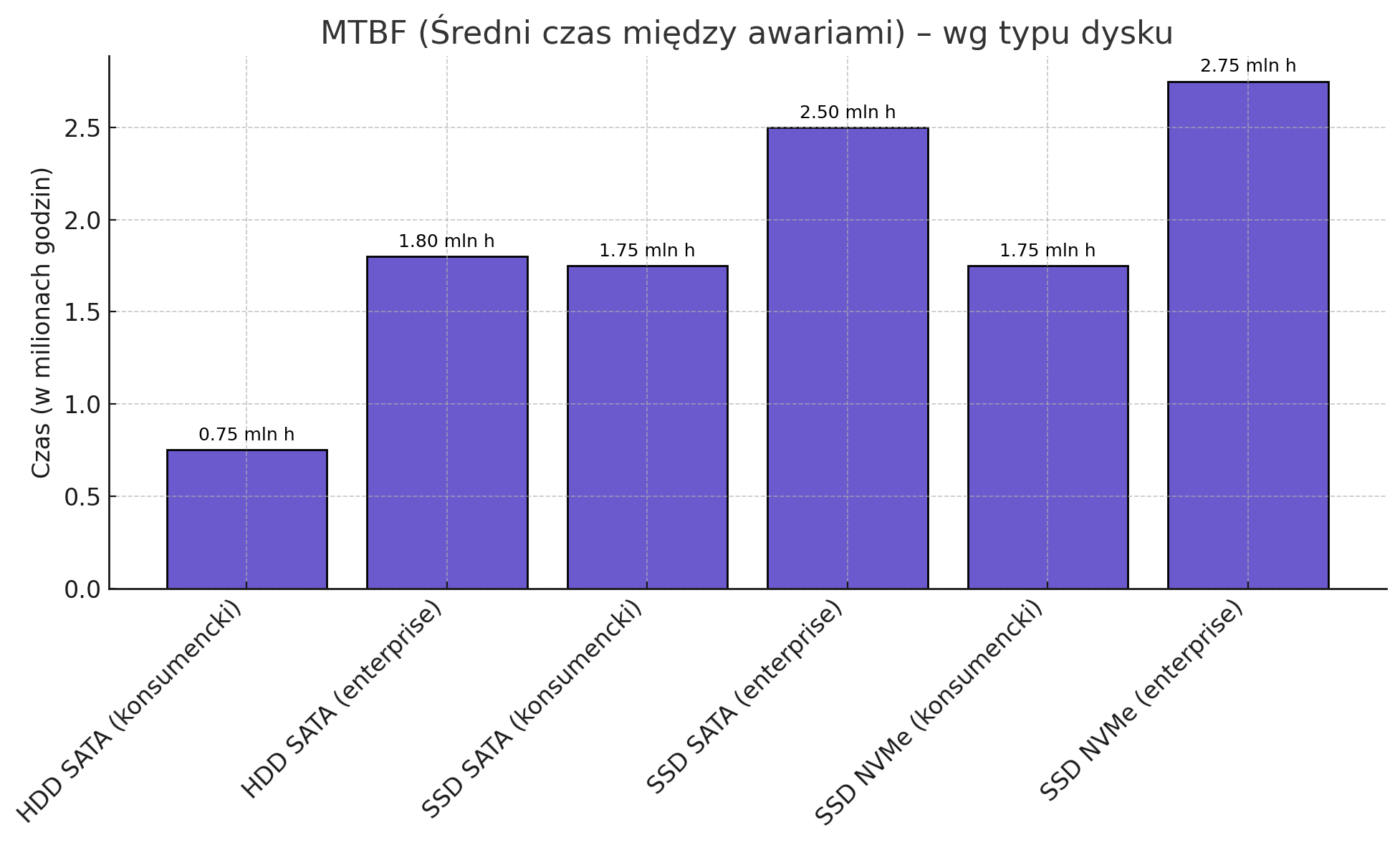
MTBF – Mean Time Between Failures
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) is a statistical measure of the average time between device failures.Consumer HDD:
- • MTBF: 500,000 – 1,000,000 hours
Enterprise HDD:
- • MTBF: 1,200,000 – 2,500,000 hours
Consumer SATA and NVMe SSDs:
- • MTBF: 1,500,000 – 2,000,000 hours
Enterprise-class SATA and NVMe SSDs:
- • MTBF: 2,000,000 – 3,000,000 hours
Manufacturer warranty and support
The warranty period is often a good indicator of the durability of the drive:
Consumer HDD:
- • Warranty: 2-3 years
Enterprise HDD:
- • Warranty: 3-5 years
Consumer SATA SSD:
- • Warranty: 3-5 years
Consumer NVMe:
- • Warranty: 5 years
Enterprise-class SSD and NVMe:
- • Warranty: 5 years, often with the possibility of extension
It is worth noting that Samsung 980 drives offer a 5-year warranty, which proves their reliability. high quality and reliability.
Hardware compatibility – what to pay attention to?
Before purchasing a drive, make sure it is compatible with your existing or planned hardware.NVMe Drive Requirements
To use NVMe drives, you need:- Motherboards with M.2 slot – check if your motherboard has an M.2 slot with NVMe support (not all M.2 slots support NVMe)3
- The appropriate PCIe version – for full performance:
- • PCIe 3.0 drives require a PCIe 3.0 capable motherboard
- • PCIe 4.0 drives require a PCIe 4.0 capable motherboard
- • PCIe 5.0 drives require the latest PCIe 5.0 capable motherboards
- Operating system with NVMe support – newer versions of Windows, Linux, and macOS have built-in support, but older systems may require additional drivers
Limitations of Legacy Systems
Older Systems may have the following limitations:- No M.2 slots -most pre-2015 motherboards do not have M.2 slots
- Limited to SATA -some older M.2 slots only support SATA M.2 drives, not NVMe
- No support for booting from NVMe -Older BIOSes may not allow booting from NVMe drive
Upgrade options
It is worth considering future expansion options:- PCIe adapter cards – allow you to install an NVMe drive in a computer without native M.2 slots, via a PCIe slot
- External NVMe Enclosures – allow you to connect an NVMe drive via USB 3.2 or Thunderbolt
- M.2 to SATA Adapters – allows you to connect an M.2 SATA drive to a standard SATA connector (does not work with NVMe)
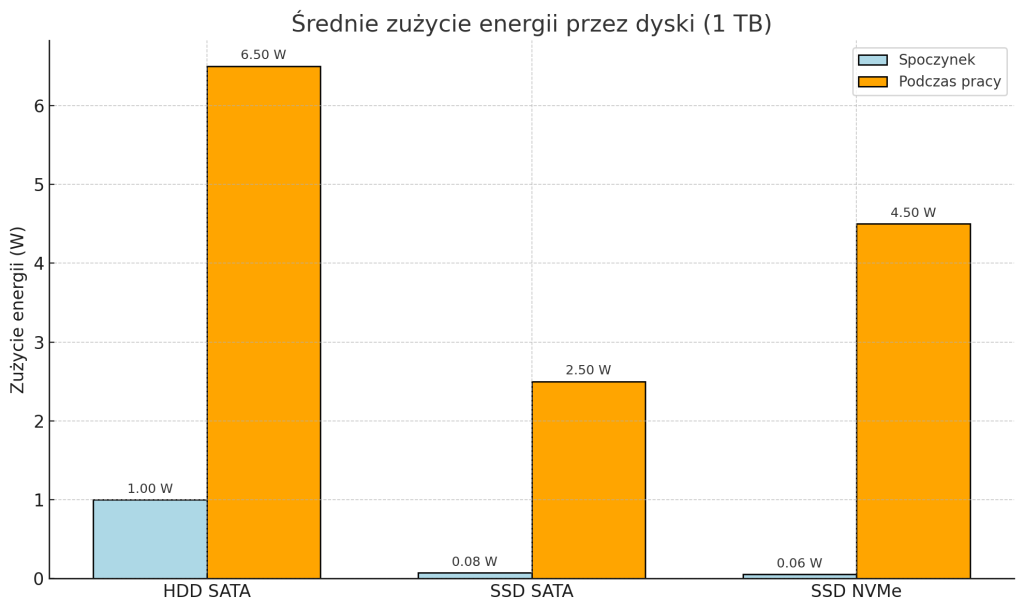
Energy consumption and cooling issues
The energy and thermal aspects of disks are important for both individual workstations and large server installations.Impact on electricity bill
Average power consumption for 1TB drives:HDD SATA:
- • At rest: 0.8-1.2 W
- • During operation: 5-8 W
SSD SATA:
- • At rest: 0.05-0.1 W
- • During operation: 2-3 W
NVMe:
- • At rest: 0.03-0.08 W
- • In operation: 2-7 W (depending on model and load)
Noise and temperature in the office environment
HDD SATA:
- • Generates audible noise during operation (25-30 dB)
- • Produces more heat
- • May require additional cooling in the housing
SATA and NVMe SSDs:
- • Silent operation
- • Lower heat generation (although high-performance NVMe can get quite hot)
- • Improving work comfort in the office environment
It’s worth noting that modern NVMe drives often feature heat-dissipating features, such as the nickel designs used by Samsung, which help maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Performance optimization – how to choose the right solution?
The most expensive solution isn't always the best for a company's specific needs. Below are strategies to optimize performance and costs.Analysis of company needs
Before choosing a disk technology, it is worth analyzing:- Type of operations performed – if the company mainly processes large files sequentially (e.g. video), even basic NVMe will provide significant performance improvements
- I/O Operation Intensity – for databases and multitasking environments, the high IOPS values offered by NVMe are crucial
- Budget – sometimes it is better to invest in a smaller but faster system disk than in a larger but slower one
- Load profile – Data intensive applications can benefit from drives with higher TBW
Hybrid disk solutions
To optimize the performance-to-cost ratio, many companies choose hybrid solutions:- NVMe + HDD – fast NVMe disk for system and applications, cheaper HDD for data
- Tiered Storage – automatic transfer of frequently used data to faster media
- Caching – using a smaller, faster drive to store the most frequently used data
Data storage strategies
Depending on the type of data and access frequency, different strategies can be used:- Critical, frequently used data -NVMe PCIe 4.0/5.0
- Application data and operating systems -NVMe PCIe 3.0 or good quality SATA SSD
- Archives and rarely used data – HDD in RAID arrays for increased reliability
Future trends and technology developments
The disk technology market is constantly evolving. Here are some trends to consider when planning future investments.What awaits us in the coming years?
- PCIe 5.0 and 6.0 adoption – even higher transfer speeds, exceeding 20 GB/s
- NVMe prices drop – NVMe technology is becoming more affordable, replacing traditional SATA SSDs
- Increased durability – new generations of flash memory offer an increasing number of write cycles
- Intelligent data management – drives with built-in artificial intelligence algorithms to optimize data access and storage
- In-Storage Processing (ISP) – drives with built-in processors and accelerators for processing data without having to send it to the CPU
When is it best to wait to buy?
When planning corporate purchases, it is worth considering the technology life cycle:- New Generations of PCIe – if you are planning to modernize your entire infrastructure, it may be worth waiting for the PCIe 5.0 standard to become widespread
- Price drops – usually after the introduction of a new generation, the prices of the previous one drop significantly
- End of fiscal year – this is often when the best promotions for business equipment appear

Summary and recommendations
After a detailed analysis of the various disk technologies, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- For typical office applications:
- • We recommend SATA SSDs or basic NVMe PCIe 3.0 drives
- • They offer significant performance improvements over HDD at a moderate cost
- • You may want to consider an additional HDD for storing large archives
- For workstations and development computers:
- • We highly recommend NVMe PCIe 4.0 drives
- • They provide excellent responsiveness and short application loading times
- • They allow for smooth work even with intensive tasks
- For servers and database environments:
- • Enterprise-class NVMe PCIe 4.0/5.0 drives required
- • High throughput and IOPS are crucial to handle many simultaneous operations
- • It is worth considering solutions with redundancy to increase reliability
- For multimedia processing stations:
- • High-capacity NVMe PCIe 5.0 drives are best
- • Fast transfer of large files significantly increases productivity
- • You may want to consider configuring RAID 0 for even better performance
Ultimately, the investment in faster drives (especially moving from HDD to SSD) almost always pays off in a business environment through increased productivity, reduced downtime, and longer hardware life.
Choosing the right storage solution can be complicated, especially given your company's specific needs. Our company specializes in consulting on IT infrastructure for businesses.
We offer:
- • Professional analysis of your company's needs
- • Selection of optimal disk solutions tailored to the specific nature of the business
- • Comprehensive implementation, including data migration
- • Long-term support and service
Don't risk costly downtime and data loss - we'll help you choose a solution that will be the best compromise between performance, reliability and cost, tailored to the specific needs of your organization.
Contact us to take your business to the next level!




